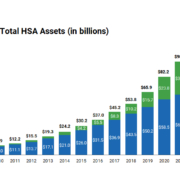
Trump’s “One Big Beautiful Bill” (OBBB), passed on July 4, 2025, initially promised significant changes to Health Savings Accounts (HSAs). However, the final version of the legislation contained modest updates to HSA policy. Current HSA holders get to keep what they have, but significant reforms such as extending eligibility to those on Medicare or relaxing contribution restrictions, were abandoned in negotiations. Instead, the bill primarily focuses on restructuring Medicaid and welfare programs, implementing work mandates, and providing tax credits tied to families and newborn savings accounts.
Health Saving Accounts were thought to have a larger presence in the bill that would have placed HSAs as a centerpiece of healthcare funding and provided areas for growth by softening regulations of who can contribute, such as those on Medicare Part A. Without eligibility expansion, HSAs remain mostly unchanged, and tax-advantaged growth remains limited to current users.
Here’s a breakdown of what changes OBBB brings to HSA plans:
- If you are enrolled in a Bronze or Catastrophic ACA plan, you are now eligible to contribute to HSAs starting January 1, 2026.
- HSA funds can be used for Direct Primary Care (DPC) arrangements. DPCs typically follow the model of a monthly fee, which covers office visits prior to meeting the HDHP deductible. With OBBB, these monthly fees now fall under qualified HSA expenses if they do not exceed $150/month for an individual or $300/month for families.
- First-dollar coverage for telehealth services no longer disqualifies HSA status, which allows plans to provide low or no-cost telehealth services before satisfying your deductible if you are enrolled in a qualified HDHP without using your HSA contributions.
HSAs remain a useful tool for eligible taxpayers and serve as a tax-savings vehicle.
Triple Tax Advantage
- Pre-tax Contributions – Money goes in tax-free, reducing your taxable income
- Tax-free Growth – Funds grow tax-deferred through interest and/or investments (no capital gains)
- Tax-Free Withdrawals – As long as funds are used for qualified medical expenses, withdrawals are tax-free
Saving for the Future
- You can invest your HSA balance (once you hit a threshold set by your carrier, allowing it to grow like a retirement account)
- Can be used in retirement tax-free for medical expenses, or after age 65, for any reason (income taxes apply only if not used for qualifying healthcare expenses)
HSA funds roll over year-to-year, and don’t have a use-it-or-lose-it rule like Flexible Spending Accounts (FSAs). Additionally, you can use your HSA funds for a wide range of expenses, including copays, prescriptions, dental and vision care, mental health services, and certain over-the-counter items (such as pain relievers, allergy medications, and first-aid supplies). Lastly, you OWN your HSA – it stays with you if you change jobs or retire. You control how and when it is used, allowing you to learn how they work and ensure you make the most out of the account.
While the “One Big Beautiful Bill” fell short of delivering the HSA expansion many had hoped for, it did make some notable improvements. It’s clear that Health Savings Accounts remain one of the most innovative tools for managing healthcare costs, both now and in the future. In today’s uncertain and costly healthcare environment, understanding and maximizing your HSA is essential. For those enrolled in an HSA, remember, it isn’t just a spending account — it’s a strategy.
Posted by CalCPA Health | July 2025